
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
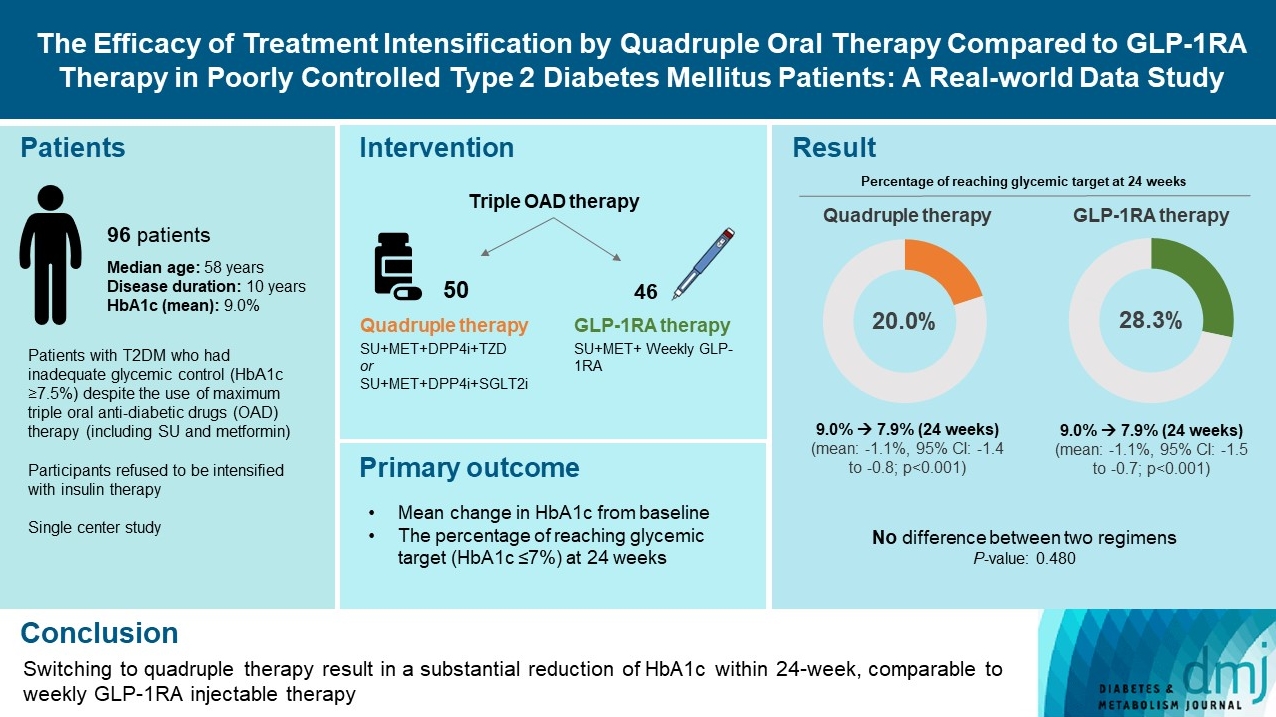
- The Efficacy of Treatment Intensification by Quadruple Oral Therapy Compared to GLP-1RA Therapy in Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Real-World Data Study
- Minyoung Kim, Hosu Kim, Kyong Young Kim, Soo Kyoung Kim, Junghwa Jung, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Jaehoon Jung, Jong Ha Baek
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):135-139. Published online April 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0373
- 7,533 View
- 296 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - We compared the glycemic efficacy of treatment intensification between quadruple oral antidiabetic drug therapy and once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA)-based triple therapy in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus refractory to triple oral therapy. For 24 weeks, changes in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) from baseline were compared between the two treatment groups. Of all 96 patients, 50 patients were treated with quadruple therapy, and 46 were treated with GLP-1RA therapy. Reductions in HbA1c for 24 weeks were comparable (in both, 1.1% reduction from baseline; P=0.59). Meanwhile, lower C-peptide level was associated with a lower glucose-lowering response of GLP-1RA therapy (R=0.3, P=0.04) but not with quadruple therapy (R=–0.13, P=0.40). HbA1c reduction by GLP-1RA therapy was inferior to that by quadruple therapy in the low C-peptide subgroup (mean, –0.1% vs. –1.3%; P=0.04). Treatment intensification by switching to quadruple oral therapy showed similar glucose-lowering efficacy to weekly GLP-1RA-based triple therapy. Meanwhile, the therapeutic response was affected by C-peptide levels in the GLP-1RA therapy group but not in the quadruple therapy group.
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jong Ha Baek, Woo Je Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Soo Kyoung Kim, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):46-54. Published online July 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0134
- 6,813 View
- 230 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
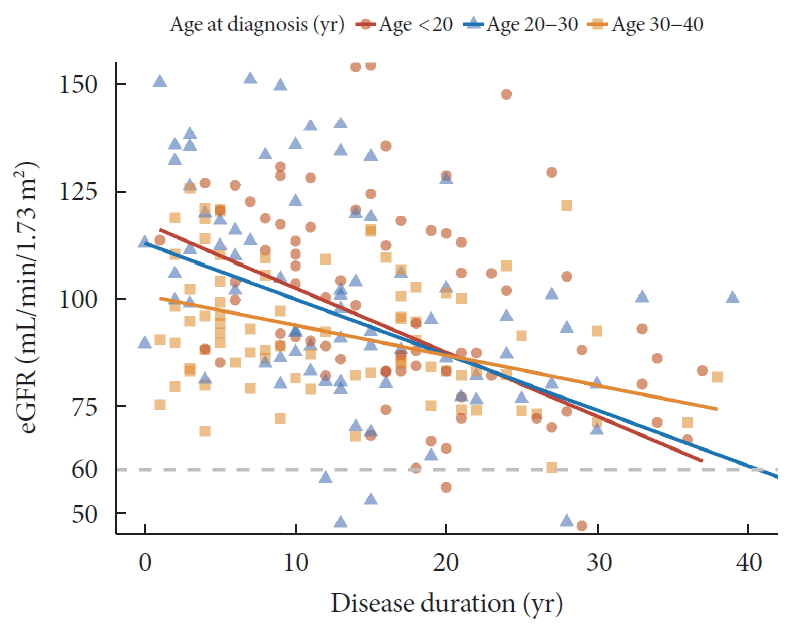
ePub Background The aim of this study was to evaluate characteristics and risk of diabetic complications according to age at diagnosis among young adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).
Methods A total of 255 T1DM patients aged less than 40 years were included. Patients were categorized into three groups (<20, 20 to 29, and 30 to 40 years) according to age at diagnosis. Diabetic nephropathy (DN) was defined when spot urine-albumin creatinine ratio was 300 mg/g or more and/or estimated glomerular filtration ratio (eGFR) level was 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or less.
Results Median age at diagnosis was 25 years and disease duration was 14 years. Individuals diagnosed with T1DM at childhood/adolescent (age <20 years) had lower stimulated C-peptide levels. They received more intensive insulin treatment with higher total daily insulin doses compared to older onset groups. The prevalence of DN was higher in the childhood/adolescent-onset group than in older onset groups (25.3% vs. 15.3% vs. 9.6%,
P =0.022). The eGFR was inversely associated with disease duration whilst the degree of decrease was more prominent in the childhood/adolescent-onset group than in the later onset group (aged 30 to 40 years;P <0.001). Childhood/adolescent-onset group was independently associated with the risk of DN compared to the older onset group (aged 30 to 40 years; odds ratio, 3.47; 95% confidence interval, 1.45 to 8.33;P =0.005).Conclusion In individuals with childhood/adolescent-onset T1DM, the reduction in renal function is more prominent with disease duration. Early age-onset T1DM is an independent risk of DN.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Age at onset of type 1 diabetes between puberty and 30 years old is associated with increased diabetic nephropathy risk
Yen-Bo Lin, Wayne Huey-Herng Sheu, Su-Huey Lo, Yen-Po Yeh, Chien-Ning Huang, Chii-Min Hwu, Chang-Hsun Hsieh, Horng-Yi Ou, Lee-Ming Chuang, Jung-Fu Chen, Yu-Cheng Chen, Yun-Hsing Peng, Szu-Tah Chen, Shang-Ren Hsu, Yi-Ling Hsieh, Chih-Hsun Chu, Chieg-Hsiang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeted mapping and utilization of the perihepatic surface for therapeutic beta cell replacement and retrieval in diabetic non-human primates
David J. Leishman, Scott H. Oppler, Laura L. Hocum Stone, Timothy D. O’Brien, Sabarinathan Ramachandran, Bradley J. Willenberg, Andrew B. Adams, Bernhard J. Hering, Melanie L. Graham
Frontiers in Transplantation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Eun Seok Kang, Soo Heon Kwak, Yeoree Yang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyun Bae, Jun Sung Moon, Chang Hee Jung, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh, Sun Joon Moon, Sun Ok Song, Suk Chon, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Network-based identification and prioritization of key transcriptional factors of diabetic kidney disease
Ikhlak Ahmed, Mubarak Ziab, Sahar Da’as, Waseem Hasan, Sujitha P. Jeya, Elbay Aliyev, Sabah Nisar, Ajaz A. Bhat, Khalid Adnan Fakhro, Ammira S. Alshabeeb Akil
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2023; 21: 716. CrossRef - Comparison of diabetes distress and depression screening results of emerging adults with type 1 diabetes onset at different ages: findings from the German early-onset T1D study and the German Diabetes Study (GDS)
Anna Stahl-Pehe, Christina Bächle, Kálmán Bódis, Oana-Patricia Zaharia, Karin Lange, Reinhard W. Holl, Michael Roden, Joachim Rosenbauer, M. Roden, H. Al-Hasani, B Belgardt, GJ. Bönhof, V Burkart, A. E. Buyken, G. Geerling, C. Herder, A. Icks, K. Jandelei
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hemoperfusion and functional state of the macula after simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation
IV Vorobyeva, EV Bulava, LK Moshetova, AV Pinchuk
Bulletin of Russian State Medical University.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sigesbeckia orientalis Extract Ameliorates the Experimental Diabetic Nephropathy by Downregulating the Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Signaling Pathways
Chung-Ming Chen, Jer-Yiing Houng, Tsui-Ling Ko, Shu-Hui Juan, Hsiu-Chu Chou, Xing Li
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Impact of low-protein diet on cardiovascular risk factors and kidney function in diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials
Mohammad Hassan Sohouli, Parvin Mirmiran, Shaikh Sanjid Seraj, Emad Kutbi, Hadil Ali Mohammed Alkahmous, Faisal Almuqayyid, Omar Ahnaf Arafah, Abdul Rahman Riad Barakeh, Ahmed Abu-Zaid
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110068. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Jong Ha Baek, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 281. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 277. CrossRef - Role of magnetic resonance diffusion weighted imaging in diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy in children living with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Eman Nabil Wahba, Ashraf Elsharkawy, Mohammad Hosny Awad, Ashraf Abdel Rahman, Amr Sarhan
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 34(12): 1585. CrossRef
- Age at onset of type 1 diabetes between puberty and 30 years old is associated with increased diabetic nephropathy risk
- Clinical Care/Education
- Re-Evaluation of Efficacy of Moderate-Intensity Statins in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Soo Kyoung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(1):20-22. Published online February 16, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.1.20
- 3,046 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal attainment rates in high-risk patients with cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
Ye Seul Yang, Bo Ram Yang, Mi-Sook Kim, Yunji Hwang, Sung Hee Choi
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in Korean patients with hypercholesterolemia and high cardiovascular risk: subanalysis of the ODYSSEY-KT study
Chang-Wook Nam, Dong-Soo Kim, Jianyong Li, Marie T. Baccara-Dinet, Ivy Li, Ji-Hyun Kim, Chong-Jin Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2019; 34(6): 1252. CrossRef
- Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal attainment rates in high-risk patients with cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Serum Calcium and the Risk of Incident Metabolic Syndrome: A 4.3-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study
- Jong Ha Baek, Sang-Man Jin, Ji Cheol Bae, Jae Hwan Jee, Tae Yang Yu, Soo Kyoung Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(1):60-68. Published online December 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.1.60
- 4,079 View
- 32 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background An association between serum calcium level and risk of metabolic syndrome (MetS) has been suggested in cross-sectional studies. This study aimed to evaluate the association between baseline serum calcium level and risk of incident MetS in a longitudinal study.
Methods We conducted a retrospective longitudinal study of 12,706 participants without MetS who participated in a health screening program, had normal range serum calcium level at baseline (mean age, 51 years), and were followed up for 4.3 years (18,925 person-years). The risk of developing MetS was analyzed according to the baseline serum calcium levels.
Results A total of 3,448 incident cases (27.1%) of MetS developed during the follow-up period. The hazard ratio (HR) for incident MetS did not increase with increasing tertile of serum calcium level in an age- and sex-matched model (
P for trend=0.915). The HRs (95% confidence interval [CI]) for incident MetS comparing the second and the third tertiles to the first tertile of baseline serum calcium level were 0.91 (95% CI, 0.84 to 0.99) and 0.85 (95% CI, 0.78 to 0.92) in a fully adjusted model, respectively (P for trend=0.001). A decreased risk of incident MetS in higher tertiles of serum calcium level was observed in subjects with central obesity and/or a metabolically unhealthy state at baseline.Conclusion There was no positive correlation between baseline serum calcium levels and incident risk of MetS in this longitudinal study. There was an association between higher serum calcium levels and decreased incident MetS in individuals with central obesity or two components of MetS at baseline.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Independent associations of serum calcium with or without albumin adjustment and serum phosphorus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: results from NHANES 1999-2018
Haolong Qi, Bin Wang, Lei Zhu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of the serum calcium level with metabolic syndrome and its components among adults in Taiwan
Jer-min Chen, Tai-yin Wu, Yi-fan Wu, Kuan-liang Kuo
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Elevated Chinese visceral adiposity index increases the risk of stroke in Chinese patients with metabolic syndrome
Zeyu Liu, Qin Huang, Bi Deng, Minping Wei, Xianjing Feng, Fang Yu, Jie Feng, Yang Du, Jian Xia
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metformin: Expanding the Scope of Application—Starting Earlier than Yesterday, Canceling Later
Yulia A. Kononova, Nikolai P. Likhonosov, Alina Yu. Babenko
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(4): 2363. CrossRef - Metformin in prediabetes: key mechanisms for the prevention of diabetes and cardiometabolic risks
A. Yu. Babenko
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (10): 96. CrossRef Calcium and Phosphate Levels are Among Other Factors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Normal Weight
Kamila Osadnik, Tadeusz Osadnik, Marcin Delijewski, Mateusz Lejawa, Martyna Fronczek, Rafał Reguła, Mariusz Gąsior, Natalia Pawlas
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 1281. CrossRef- Association between selected trace elements and body mass index and waist circumference: A cross sectional study
Mahnaz Zohal, Saeedeh Jam-Ashkezari, Nasim Namiranian, Amin Moosavi, Akram Ghadiri-Anari
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(2): 1293. CrossRef - Letter: Increased Serum Angiopoietin-Like 6 Ahead of Metabolic Syndrome in a Prospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:521-9)
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(5): 727. CrossRef - Genotype effects of glucokinase regulator on lipid profiles and glycemic status are modified by circulating calcium levels: results from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Oh Yoen Kim, So-Young Kwak, Hyunjung Lim, Min-Jeong Shin
Nutrition Research.2018; 60: 96. CrossRef
- Independent associations of serum calcium with or without albumin adjustment and serum phosphorus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: results from NHANES 1999-2018
- Effectiveness of 3-Day Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Improving Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Clinical Practice
- Soo Kyoung Kim, Hye Jeong Kim, Taehun Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Sun Wook Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee, Yong-Ki Min, Kwang-Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(6):449-455. Published online December 15, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.6.449
- 4,871 View
- 38 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study was to investigate whether adjusting diabetic treatment regimens according to the information obtained from a continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) might lead to improved glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods We reviewed the medical charts of 172 patients who used the CGMS for 1 year starting in December 2008 and the records of 1,500 patients who visited their regular outpatient clinics during December 2008. Of these patients, a total of 65 CGMS patients and 301 regular outpatients (control group) were enrolled in the study after propensity score matching. There were no differences in baseline glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), age, and duration of diabetes between the CGMS and the control groups after propensity score matching. The changes in the HbA1c levels from baseline to 6 months were calculated.
Results The CGMS group showed a significant improvement in the HbA1c level compared to the control group at 3 months (7.9%±1.6% vs. 7.4%±1.2%,
P =0.001) and at 6 months (7.4%±1.2% vs. 7.9%±1.6%,P =0.010). There were significant differences in the treatment modality changes between the CGMS group and the control group.Conclusion Using a 3-day CGMS was advantageous for improving glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes and may help these patients to optimize glycemic control in clinical practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biological and Clinical Impacts of Glucose Metabolism in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Zhao Liu, Hiromitsu Hayashi, Kazuki Matsumura, Norio Uemura, Yuta Shiraishi, Hiroki Sato, Hideo Baba
Cancers.2023; 15(2): 498. CrossRef - Professional continuous glucose monitoring in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sergio Di Molfetta, Irene Caruso, Angelo Cignarelli, Annalisa Natalicchio, Sebastio Perrini, Luigi Laviola, Francesco Giorgino
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(5): 1301. CrossRef - American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: The Use of Advanced Technology in the Management of Persons With Diabetes Mellitus
George Grunberger, Jennifer Sherr, Myriam Allende, Thomas Blevins, Bruce Bode, Yehuda Handelsman, Richard Hellman, Rosemarie Lajara, Victor Lawrence Roberts, David Rodbard, Carla Stec, Jeff Unger
Endocrine Practice.2021; 27(6): 505. CrossRef - Lack of Acceptance of Digital Healthcare in the Medical Market: Addressing Old Problems Raised by Various Clinical Professionals and Developing Possible Solutions
Jong Il Park, Hwa Young Lee, Hyunah Kim, Jisan Lee, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A head‐to‐head comparison of personal and professional continuous glucose monitoring systems in people with type 1 diabetes: Hypoglycaemia remains the weak spot
Othmar Moser, Marlene Pandis, Felix Aberer, Harald Kojzar, Daniel Hochfellner, Hesham Elsayed, Melanie Motschnig, Thomas Augustin, Philipp Kreuzer, Thomas R. Pieber, Harald Sourij, Julia K. Mader
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(4): 1043. CrossRef - Glucose monitoring in diabetes: from clinical studies to real‐world practice
Rebecca C Sagar, Afroze Abbas, Ramzi Ajjan
Practical Diabetes.2019; 36(2): 57. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review of Literature and Meta-analysis
Cindy Park, Quang A. Le
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2018; 20(9): 613. CrossRef - Effects of Dapagliflozin on 24-Hour Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Robert R. Henry, Poul Strange, Rong Zhou, Jeremy Pettus, Leon Shi, Sergey B. Zhuplatov, Traci Mansfield, David Klein, Arie Katz
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2018; 20(11): 715. CrossRef - Clinical and economic benefits of professional CGM among people with type 2 diabetes in the United States: analysis of claims and lab data
Joseph A. Sierra, Mona Shah, Max S. Gill, Zachery Flores, Hiten Chawla, Francine R. Kaufman, Robert Vigersky
Journal of Medical Economics.2018; 21(3): 225. CrossRef - Role of continuous glucose monitoring for type 2 in diabetes management and research
Robert Vigersky, Maneesh Shrivastav
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(1): 280. CrossRef - Assessing the Therapeutic Utility of Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 2 Diabetes Across Various Therapies: A Retrospective Evaluation
Jothydev Kesavadev, Robert Vigersky, John Shin, Pradeep Babu Sadasivan Pillai, Arun Shankar, Geethu Sanal, Gopika Krishnan, Sunitha Jothydev
Advances in Therapy.2017; 34(8): 1918. CrossRef - Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Youth-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Christine L. Chan
Current Diabetes Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The efficacy and safety of adding either vildagliptin or glimepiride to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Gyuri Kim, Sewon Oh, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2017; 18(12): 1179. CrossRef - Morning Spot Urine Glucose-to-Creatinine Ratios Predict Overnight Urinary Glucose Excretion in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
So Ra Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Sang-Guk Lee, Sun Hee Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Jeong-Ho Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2017; 37(1): 9. CrossRef - The Contemporary Role of Masked Continuous Glucose Monitoring in a Real-Time World
Ian Blumer
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2016; 10(3): 790. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability: How Do We Measure It and Why Is It Important?
Sunghwan Suh, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 273. CrossRef
- Biological and Clinical Impacts of Glucose Metabolism in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- Clinical Significance of the Presence of Autonomic and Vestibular Dysfunction in Diabetic Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy
- Soo Kyoung Kim, Kyeong Ju Lee, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Sang Min Lee, Tae Sik Jung, Jung Hwa Jung, Sungsu Kim, Deok Ryong Kim, Seong-Ki Ahn, Won-Hee Choi, Soon Il Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(1):64-69. Published online February 17, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.1.64
- 3,844 View
- 46 Download
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated the prevalence of diabetic autonomic neuropathy (DAN) and vestibular dysfunction (VD) in diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy.
Methods Thirty-five diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy were enrolled from August 2008 to July 2009. All subjects underwent autonomic function tests. Nineteen of the patients (54.3%) underwent videonystagmography.
Results Diabetic autonomic neuropathy was observed in 28 patients (80%). A mild degree of autonomic failure was observed in 18 patients (64.3%), and a moderate degree of autonomic failure was observed in ten patients (35.7%). Factors related to DAN included diabetic nephropathy (
P =0.032), degree of chronic kidney disease (P =0.003), and duration of diabetes (P =0.044). Vestibular dysfunction was observed in 11 of 19 patients (57.9%). There was no significant association between DAN and VD.Conclusion Diabetic autonomic neuropathy was observed in 28 diabetic patients (80%) with peripheral neuropathy. Vestibular dysfunction was observed in nearly 60% of diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy who complained of dizziness but showed no significant association with DAN. Diabetic patients who complained of dizziness need to examine both autonomic function and vestibular function.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- β-Glucans obtained from fungus for wound healing: A review
Chunhua Xu, Fengxia Wang, Shibing Guan, Lizhen Wang
Carbohydrate Polymers.2024; 327: 121662. CrossRef - Dynamic and static balance functions in hemodialysis patients and non‐dialysis dependent CKD patients
Nobuyuki Shirai, Suguru Yamamoto, Yutaka Osawa, Atsuhiro Tsubaki, Shinichiro Morishita, Ichiei Narita
Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis.2023; 27(3): 412. CrossRef - Micro (mi) RNA and Diabetic Retinopathy
Sadashiv, Praveen Sharma, Shailendra Dwivedi, Sunita Tiwari, Pankaj Kumar Singh, Amit Pal, Sandeep Kumar
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry.2022; 37(3): 267. CrossRef - Physiotherapists’ Perspectives on Type 2 Diabetes Management and as a Primary Condition for Referral to Physiotherapy Services: A Qualitative Descriptive Study
Sarah M. Janssen, Denise M. Connelly, Heather Gillis
Physiotherapy Canada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Subclinical vestibular dysfunction in type 1 diabetes mellitus
Abdollah Moossavi, Moslem Shaabani, Ensieh Nasli Esfahani, Mohsen Vahedi, Zakaria Enayati
Hearing, Balance and Communication.2021; 19(2): 86. CrossRef Potential Applications of Nanomaterials and Technology for Diabetic Wound Healing
Que Bai, Kai Han, Kai Dong, Caiyun Zheng, Yanni Zhang, Qianfa Long, Tingli Lu
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 9717. CrossRef- Recent advancements in biopolymer and metal nanoparticle-based materials in diabetic wound healing management
Veena Vijayakumar, Sushanta K. Samal, Smita Mohanty, Sanjay K. Nayak
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2019; 122: 137. CrossRef - Auditory function and motor proficiency in type 1 diabetic children: A case-control study
Jalali Mir Mohammad, Soleimani Robabeh, Koohmanai Shahin, Tizno Saeed, Akbari Maryam
International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology.2018; 109: 7. CrossRef - Vestibular profile of type 1 versus type 2 chronic diabetes mellitus
Ola Abdallah Ibraheem, Mohammad Ramadan Hassaan, Mayada Mohamed Mousa
Hearing, Balance and Communication.2017; 15(3): 133. CrossRef - Glycemic variability is an important risk factor for cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients
Wen Xu, Yanhua Zhu, Xubin Yang, Hongrong Deng, Jinhua Yan, Shaoda Lin, Huazhang Yang, Hong Chen, Jianping Weng
International Journal of Cardiology.2016; 215: 263. CrossRef - Impact of Diabetic Complications on Balance and Falls: Contribution of the Vestibular System
Linda J. D'Silva, James Lin, Hinrich Staecker, Susan L. Whitney, Patricia M. Kluding
Physical Therapy.2016; 96(3): 400. CrossRef - Shedding light on miR-26a: Another key regulator of angiogenesis in diabetic wound healing
Carlos Zgheib, Kenneth W. Liechty
Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology.2016; 92: 203. CrossRef - Augmented asymmetrical visual field dependence in asymptomatic diabetics: Evidence of subclinical asymmetrical bilateral vestibular dysfunction
Rima Abdul Razzak, Jeffery Bagust, Sharon Docherty, Wiam Hussein, Abdullah Al-Otaibi
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2015; 29(1): 68. CrossRef - Associations between autonomic dysfunction and pain in chemotherapy‐induced polyneuropathy
H. Nahman‐Averbuch, Y. Granovsky, E. Sprecher, M. Steiner, T. Tzuk‐Shina, D. Pud, D. Yarnitsky
European Journal of Pain.2014; 18(1): 47. CrossRef - Balance training in the intervention of fall risk in elderly with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A review
Xi Pan, Jiao-jiao Bai
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2014; 1(4): 441. CrossRef - Synkope aus der Sicht des Neurologen
A. Bickel, J. Röther
Herz.2014; 39(4): 443. CrossRef - The Role of MicroRNAs in Diabetic Complications—Special Emphasis on Wound Healing
João Moura, Elisabet Børsheim, Eugenia Carvalho
Genes.2014; 5(4): 926. CrossRef - Recent advances on the development of wound dressings for diabetic foot ulcer treatment—A review
Liane I.F. Moura, Ana M.A. Dias, Eugénia Carvalho, Hermínio C. de Sousa
Acta Biomaterialia.2013; 9(7): 7093. CrossRef
- β-Glucans obtained from fungus for wound healing: A review
- Response: The Relationship between Lung Function and Metabolic Syndrome in Obese and Non-Obese Korean Adult Males (Korean Diabetes J 2010;34:253-60)
- Soo Kyoung Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(5):329-330. Published online October 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.5.329
- 2,481 View
- 25 Download
- The Relationship between Lung Function and Metabolic Syndrome in Obese and Non-Obese Korean Adult Males
- Soo Kyoung Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Yoon Ho Choi, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Hee Kyung Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee, Yong-Ki Min, Kwang-Won Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(4):253-260. Published online August 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.4.253
- 4,274 View
- 32 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The existence of an association between lung function and metabolic syndrome (MetS) has been debated in cases involving non-obese subjects. To address this debate, we performed a cross-sectional study to investigate the association between lung function and MetS in both obese and non-obese populations.
Methods The present study consisted of a total of 1,951 Korean male subjects. In this study group, we investigated relationships between lung function and MetS risk factors such as fasting serum glucose, systolic blood pressure (SBP), insulin resistance index, waist circumference (WC), and hemoglobin A1C level.
Results Forced vital capacity (FVC) values were significantly lower in the MetS group compared with those of the non-MetS group. In both non-obese (body mass index [BMI] < 25 kg/m2) and obese subjects (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2), fasting serum glucose, hemoglobin A1C level, insulin resistance index, SBP, WC, and the prevalences of diabetes and MetS were significantly higher in subjects in the lowest FVC quartile compared with those in the highest FVC quartile. Odds ratios for the presence of MetS risk factors, after adjusting for age and height, ranged from 1.21 to 1.39 (
P < 0.01) for a one standard deviation decrease in FVC.Conclusion The results of our study suggest that decreased vital capacity in Korean adult male subjects is associated with MetS, irrespective of obesity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of insulin resistance on the association between metabolic syndrome and lung function: the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Jonghoo Lee, Hye Kyeong Park, Min-Jung Kwon, Soo-Youn Ham, Hyun-Il Gil, Si-Young Lim, Jae-Uk Song
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pulmonary Function in Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis
Ning-ning Fang, Zhi-hao Wang, Shao-hua Li, Yu-yan Ge, Xin Liu, Dong-xin Sui
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(10): 606. CrossRef - Determinants of Longitudinal Change of Lung Function in Different Gender in a Large Taiwanese Population Follow-Up Study Categories: Original Investigation
Chia-Heng Chang, Szu-Chia Chen, Jiun-Hung Geng, Da-Wei Wu, Jiun-Chi Huang, Pei-Yu Wu
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(10): 1033. CrossRef - The Association between Pulmonary Functions and Incident Diabetes: Longitudinal Analysis from the Ansung Cohort in Korea
Hoon Sung Choi, Sung Woo Lee, Jin Taek Kim, Hong Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 699. CrossRef - Interactive effects of adiposity and insulin resistance on the impaired lung function in asthmatic adults: cross-sectional analysis of NHANES data
Roham Sadeghimakki, Huw David McCarthy
Annals of Human Biology.2019; 46(1): 56. CrossRef - Maternal protein restriction during lactation induces early and lasting plasma metabolomic and hepatic lipidomic signatures of the offspring in a rodent programming model
Aurore Martin Agnoux, Angélina El Ghaziri, Thomas Moyon, Anthony Pagniez, Agnès David, Gilles Simard, Patricia Parnet, El Mostafa Qannari, Dominique Darmaun, Jean-Philippe Antignac, Marie-Cécile Alexandre-Gouabau
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2018; 55: 124. CrossRef - Association between HOMA-IR and Lung Function in Korean Young Adults based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Young Bok Lee, Young Soo Kim, Dong-Hee Lee, Hee Yeon Kim, Jae-Im Lee, Hyo-Suk Ahn, Tae Seo Sohn, Tae-Kyu Lee, Jae Yen Song, Chang Dong Yeo, Mihee Hong, Kyungdo Han, Seong Cheol Jeong, Hiun Suk Chae
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Spirometric prediction equations and the relationship between metabolic syndrome and spirometric parameters from an island in Fujian, China
Yu‐Sheng Chen, Xiao‐Qin Li, Hong‐Ru Li, Xiao‐Li Yu, Feng‐Feng Lu, Li‐Ping Huang, Yan Miao, Gui‐Qing Wang, Xiao Lin, Shuang‐Qing Lian, Yun‐Hua Lin, Xiang‐E Zhang, Ting Liu, Yan‐Ling Wu
The Clinical Respiratory Journal.2017; 11(4): 514. CrossRef - Decline in lung function rather than baseline lung function is associated with the development of metabolic syndrome: A six-year longitudinal study
Soo Kyoung Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Jong-Ha Baek, Jae Hwan Jee, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Cheng Hu
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(3): e0174228. CrossRef - The relationship between serum fatty-acid binding protein 4 level and lung function in Korean subjects with normal ventilatory function
Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Seong Yong Lim, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Lung function and metabolic syndrome: Findings of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2010 肺功能与代谢综合征:2007–2010全国健康与营养调查研究结果
Earl S. Ford, Timothy J. Cunningham, Carla I. Mercado
Journal of Diabetes.2014; 6(6): 603. CrossRef - Reduced lung function is independently associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes in Korean men
Chang-Hee Kwon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jae-Uk Song, Jung-Tae Kim, Hyon Joo Kwag, Ki-Chul Sung
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2012;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter: The Relationship between Lung Function and Metabolic Syndrome in Obese and Non-Obese Korean Adult Males (Korean Diabetes J 2010;34:253-60)
Bo Kyung Koo
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(5): 327. CrossRef
- The impact of insulin resistance on the association between metabolic syndrome and lung function: the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
- Effect of Valsartan on Blood Pressure and Urinary Albumin Excretion in Hypertensive Type 2 Diabetic Patients: An Open-Label, Multicenter Study.
- Se Jun Park, Dae Jung Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Soo Yeon Park, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Hak Chul Jang, Seung Hyun Ko, Ki Ho Song, Yu Bae Ahn, Soo Kyoung Kim, Yong Wook Cho, Jun Goo Kang, Sung Hee Ihm, Cheol Young Park, Sung Woo Park, Dong Hyun Shin, Yong Hyun Kim, Kwan Woo Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(6):513-521. Published online December 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.6.513
- 2,297 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Activation of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has been an important mechanism of microvascular and macrovascular complications in diabetic patients. It has been reported that RAS blockades reduce the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether valsartan, an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), reduced blood pressure and urinary albumin excretion rate (UAER) in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. METHOD: Three hundred forty-seven hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients who had not taken angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or ARB for 6 months prior to this study were enrolled. We measured blood pressure and UAER before and after 24 weeks of valsartan treatment. RESULT: Baseline mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure was 143 +/- 15 and 87 +/- 11 mmHg, respectively and the median albumin excretion rate was 27 ug/mg. Reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure was 16 mmHg/10 mmHg and the median UAER was 19.3 ug/mg after 24 weeks (P < 0.01, respectively). When we divided the subjects into three groups according to the UAER (normoalbuminuria, microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria), significant changes were reported in the microalbuminuria and the macroalbuminuria groups. Thirty-eight (42%) patients with microalbuminuria improved to normoalbuminuria and twelve (41%) patients with macroalbuminuria improved to microalbuminuria. We found an association between the improvement of blood pressure and UAER (R = 0.165, P = 0.015). CONCLUSION: We concluded that valsartan reduces urinary albumin excretion and blood pressure in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





